Abstract:
The B3LYP/6-31+G(d,p) method was used to calculate the proton affinities of
n-alkylamines, n-alkyl thiols, and n-alcohols and the
ammonium affinities of the n-alcohols up to C-18. These affinities and
the gas-phase acidities of the n-alcohols were all found to correlate
linearly with the quotient n/(n + 1), where n is the number
of carbon atoms in the alkyl chain. This correlation leads to a limiting value
of 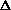 H for very long alkyl
chains: for the amines, thiols, and alcohols, the calculated maximum proton
affinities PA298,max(RX) were 938.7, 828.2, and 816.9 kJ
mol-1, respectively. The maximum ammonium affinity, -
H for very long alkyl
chains: for the amines, thiols, and alcohols, the calculated maximum proton
affinities PA298,max(RX) were 938.7, 828.2, and 816.9 kJ
mol-1, respectively. The maximum ammonium affinity, -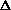 H298,max, of the
n-alcohols is 115.1 kJ mol-1.
H298,max, of the
n-alcohols is 115.1 kJ mol-1.